Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
[ad_1]
5G is choosing up acceleration. The overall put in 5G international cell websites are anticipated to broaden from 986,000 cell websites in 2021 to six.6 million cell websites in 2027 at a Compound Annual Development Price (CAGR) of 44.9%. It isn’t simply infrastructure. 5G cellular subscriptions are forecast to develop from 664 million subscribers in 2021 to 4.39 billion in 2027. Equally, the site visitors generated from 5G in 2027 is estimated to extend to six,268 exabytes and can account for 83% of all mobile site visitors. Apart from upgrading conventional community providers, 5G is enabling a spread of connectivity eventualities that may cater to not solely the prosumer market, but in addition to enterprise verticals, resembling manufacturing, healthcare and monetary providers.
Cellular backhaul hyperlinks proceed to develop
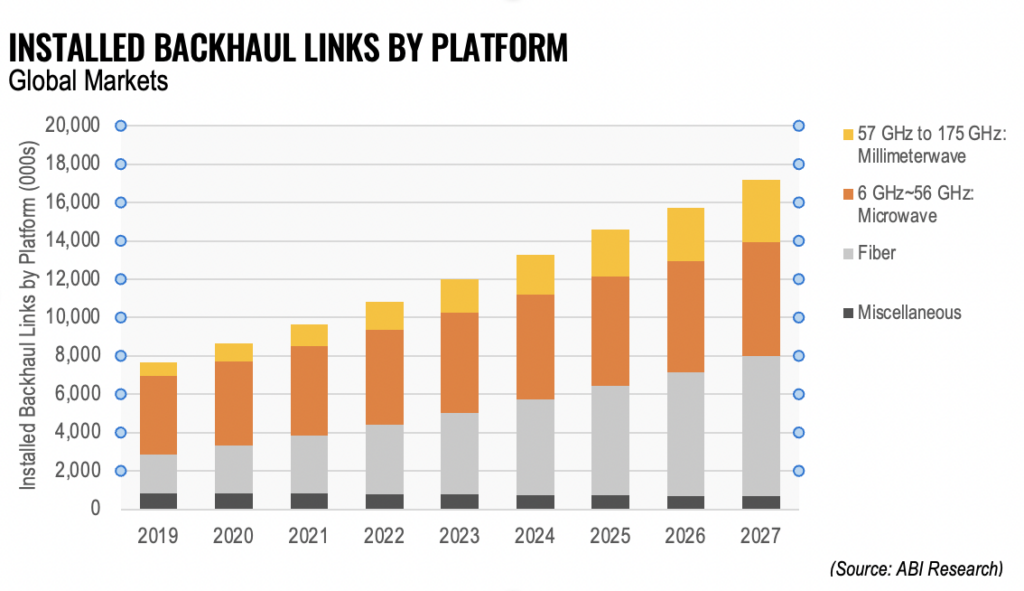
ABI Analysis forecasts that the full variety of macro cell hyperlinks will improve from round 8.1 million hyperlinks in 2021 to 11.1 million hyperlinks in 2027, whereas the variety of small cell backhaul hyperlinks will improve from 1.6 million hyperlinks in 2021 to six.1 million in 2027 at a CAGR of 25.8%. Fiber has made inroads into supporting the mobile Radio Entry Community (RAN) infrastructure of the cellular telcos, however has a Whole Price of Possession (TCO) profile that may solely be justified in sure deployment eventualities relying available on the market. Subsequently, microwave backhaul will nonetheless account for almost all of world backhaul hyperlinks from 2021 to 2027, with round 65%. Wi-fi backhaul has justified its presence out there by way of a number of improvements in spectrum use and communications applied sciences. Particularly, the usage of the E-band (71 Gigahertz (GHz) to 86 GHz), which may help wider channels, has been a sport changer.
Leveraging the E-Band
Spectrum channels are considerably bigger within the E-band — usually 500 Megahertz (MHz) to 2,000 MHz. As compared, channel sizes within the conventional microwave bands (6 GHz to 56 GHz) usually vary from 28 MHz to 56 MHz in width. Knowledge throughput for the E-band is considerably larger than the standard microwave bands. The narrower spectrum channels of conventional microwave implies that throughput is often within the order of 0.25 Gigabits per Second (Gbps) to 0.5 Gbps per channel, whereas the E-band can obtain a minimum of 3.2 Gbps to six.4 Gbps for a 500 MHz and 1 GHz channel, respectively. Extra know-how enhancements can push these eventualities even larger. Up to now, conventional microwave options (e.g., within the 15 GHz to 23 GHz bands) have been advocated, as that they had longer transmission distances. Nevertheless, utilizing the newest mmWave antennas, bonded channels, Cross Polarization (XPIC), improved modulation schemes, radio sign stabilization applied sciences, and so on. is pushing the E-band sign propagation distance past its beforehand humble ~3.5 Kilometers (km) and three.2 Gbps to six.4 Gbps knowledge throughputs:
By combining these applied sciences, Huawei has reported that its long-reach E-band resolution can attain 10 km by implementing an built-in, high-power resolution that enhances the transit energy to 24 Decibels per Milliwatt (dBm) in comparison with the trade common of 18 dBm to twenty dBm and provides knowledge throughput of 20 Gbps.
A number of transceivers
As infrastructure distributors have continued to innovate and miniaturize their electronics, the backhaul Out of doors Items (ODUs) have come down in dimension and weight. This has made backhaul gear extremely built-in, and extra viable on cell websites. As 5G site visitors throughput grows exponentially, cellular operators should resort to a number of channels wanted per cell website. Beforehand, solely the bigger macro-cell websites required such a number of channel configurations for high-traffic hyperlinks.
Historically, to hold a number of microwave channels, cellular operators would deploy a number of ODUs on a given tower, e.g., 4 ODUs for 4 frequencies. These configurations are, nevertheless, cumbersome and take up priceless antenna mount house. The most recent options from backhaul distributors like Huawei now provide as much as 4-in-1 transceivers in a single ODU. This represents a 75% discount in quantity and a 30% discount in energy consumption. This multi-transmitter and multi-receiver {hardware} design has been proactively carried out with the E-band, resembling a forthcoming 2T2R E-band transceiver with optimized twin polarization that may transmit as much as 25 Gbps with single {hardware} ODU and as much as 50 Gbps with a sophisticated A number of Enter, A number of Output (MIMO) setup.
Rural and dispersed suburban communities want backhaul
The E-band is right for central enterprise districts and concrete facilities, however rural communities, or certainly extremely dispersed small cities, typically require backhaul hops that help excessive knowledge throughput, in addition to propagation distances of 10 km to twenty km or extra. One versatile method has been to undertake a parallel hyperlink resolution that may help the capability by way of a number of bands, which is cumbersome and troublesome to deploy, whereas new improvements can allow bonding a number of bands collectively by way of compact {hardware} and a single antenna. By utilizing three mixed microwave channels (chosen from the 6, 7, 8, or 13, 15, 18 GHz bands), the cellular operator can benefit from a decrease TCO profile and maintain long-distance transmissions with knowledge throughput that may help 5G utilization. In comparison with equal standalone deployments, {hardware} prices are lowered 50% and the tower house footprint by 67%. Huawei has demonstrated this in its SuperLink resolution, which has built-in three 4-in-1 ODUs and has a single 3-in-1 antenna. Such hyperlinks can ship 10+ Gbps capability over doubtlessly 20 km.
Backhaul must be inexperienced
Because the 2021 United Nations Local weather Change Convention, a number of industries have began to comprehend they should lean into inexperienced initiatives, however in addition they want a 360º perspective. It isn’t simply the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) affect of producing the telecommunications gear that issues, but in addition the CO2 footprint of deployment and long-term upkeep. Over a 10-year interval, microwave gear ends in a 1,100 Kilogram (Kg) CO2 footprint, fiber-optic cable deployed on phone poles equates to 2,400 Kg and buried fiber ends in 4,400 Kg. The differential is the results of the extra equipment, website excavation, poured concrete, masts and conduit, and so on.
Power financial savings can be generated by way of energy consumption efficiencies, resembling by utilizing extremely built-in gear, resembling a number of transceiver ODUs and multiband antennas, for a constrained energy consumption profile. Moreover, traffic-aware methods like Huawei’s ECOwave microwave know-how can lead to 8% to 10% energy consumption financial savings.
Conclusions
5G subscriber adoption is ramping up as 5G-capable handsets have gone mainstream. 5G cell website rollouts are additionally beginning to construct up, not simply in very developed markets, however throughout geographies and demographics. Fiber-optic will stay a helpful backhaul platform for cellular telcos, however microwave and mmWave backhaul programs are proving to be important platforms for a spread of small cell and macro cell deployments in city facilities, in addition to rural communities. Traditionally, cellular operators have opted for microwave hyperlinks in conditions the place they may not deploy fiber-optic, however the speedy tempo of innovation and gear miniaturization has now opened the mmWave bands. A raft of applied sciences, resembling extremely built-in multi-transmit, multi-receive ODUs, multi-band antennas for conventional bands and an enhanced E-band vary, have improved the propagation traits considerably, whereas delivering on the much-needed 5G-capable capability.
In March 2022, The third Era Partnership Undertaking (3GPP) introduced the finalization of Launch 17. Launch 17 and Launch 18 presage a spread of “5G-Superior” options that may herald numerous upgrades for cell websites and cellular units. Launch 17 RAN upgrades embody additional enhanced huge MIMO, enhancements to the uplink management and knowledge channel design that enhance protection, potential entry to extra spectrum (24.25— 52.6 GHz as much as 71 GHz), the introduction of enhanced Built-in Entry Backhaul (IAB) to help simultaneous Transmit (Tx) and Obtain (Rx) and a simplified repeater resolution for lower-cost cell website deployments in rural areas. These developments will increase the information throughput dealt with by every cell website, however because of this, cellular operators might want to take the requisite steps to improve their backhaul infrastructure to maintain up with 3GPP and prosumer developments.
[ad_2]