Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
[ad_1]
A rising distant workforce and a wave of resignations lately have exacerbated dangers to an organization’s confidential data from insider threats. A current report from Workforce Safety Software program supplier DTEX Techniques highlights the rise of insider threats on account of the pattern towards working from wherever, catalyzed by the pandemic. In response to current knowledge, 5 million Individuals presently outline themselves as digital nomads or gig employees, and surveys constantly discover that staff are opting to maintain their versatile working patterns after the pandemic.
These traits current cybersecurity challenges, significantly with respect to insider risk. “Whereas most industries made the shift to distant work as a result of pandemic, it created new assault surfaces for cybercriminals to make the most of, equivalent to dwelling gadgets getting used for enterprise functions,” Microsoft defined of their current Digital Protection Report.
The SEI CERT Division defines insider risk as “the potential for a person who has or had approved entry to a corporation’s important property to make use of their entry, both maliciously or unintentionally, to behave in a method that might negatively have an effect on the group.” Though the strategies of assault can range, the first forms of incidents—theft of mental property (IP), sabotage, fraud, espionage, unintentional incidents, and misuse—proceed to place organizations in danger. In our work with private and non-private business, we proceed to see that insider threats are influenced by a mixture of technical, behavioral, and organizational points.
On this weblog submit, I introduce our newly revealed seventh version of the Widespread Sense Information to Mitigating Insider Threats, and spotlight and summarize a brand new finest apply that we’ve got added to this version of the information: Observe 22, Study from Previous Insider Menace Incidents. Gathering such knowledge, analyzing it, and interesting with exterior information-sharing our bodies can bolster a corporation’s insider risk-mitigation program. This exercise is crucial to making sure that analytics function successfully and that danger determinations are being made utilizing the most effective obtainable knowledge. It additionally types the inspiration for return-on-investment instances to be made for insider risk packages.
The Widespread Sense Information consists largely of twenty-two finest practices that organizations can use to handle insider danger. Every apply consists of suggestions for fast wins and high-impact options, implementation steerage, and extra sources. The practices are additionally mapped to the CERT Resilience Administration Mannequin (CERT-RMM) and safety and privateness requirements equivalent to, amongst others, ISO/IEC 27002, the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework, and—new to this version—the NIST Privateness Framework. These mappings assist establish the alignment between insider risk packages and broader cybersecurity, privateness, and risk-management frameworks, which is vital to fostering enterprise-wide collaboration.
The Widespread Sense Information springs from greater than 20 years of insider risk analysis on the SEI, a lot of it underpinned by the CERT Division’s insider risk database, which is drawn from public information of greater than 3,000 insider risk incidents. In 2005, the U.S. Secret Service sponsored the SEI’s first revealed examine of the subject. Since then, CERT analysis has helped mature the organizational practices for mitigating insider threats and managing their danger. The information has advanced with modifications within the risk panorama, technological mitigations, and shifts in data-privacy insurance policies. The seventh version continues this evolution with new and up to date practices, improved structure and imagery to reinforce usability, and extra refined phrases. It has additionally added analysis from administration science to its multidisciplinary method.
New to the seventh version of the information is Greatest Observe 22, Study from Previous Insider Menace Incidents. The apply presents steerage for growing a repository of insider traits inside a corporation and its sector. Within the the rest of this submit, I current excerpts and summaries from the complete description of the apply within the information.
Organizations that study from the previous are higher ready for the long run. Understanding how earlier incidents unfolded, whether or not within the group or elsewhere, supplies essential perception into the efficacy of present insider risk-management practices; potential gaps in prevention, detection, and response controls; and areas of emphasis for insider risk consciousness and coaching efforts.
Creating the potential to gather and analyze insider incident knowledge is a key part of an efficient insider danger administration program (IRMP) and may inform its operations, together with danger quantification, evaluation, and incident response.
Determine 1 beneath reveals how an insider risk incident repository supplies a basis for organizational preparedness.
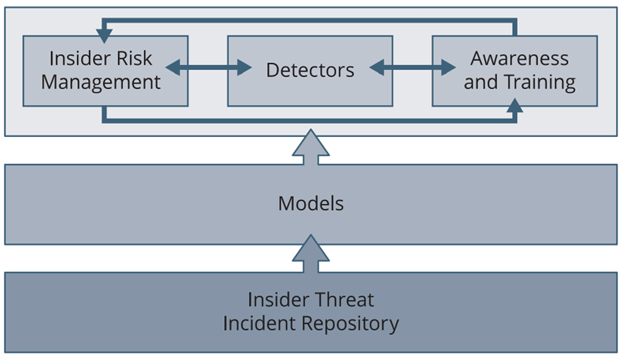
Determine 1: How Information About Earlier Insider Incidents Drives Organizational Preparedness
Having data obtainable about earlier insider incidents allows the group to derive insider risk fashions, make danger selections primarily based on historic data, and use examples of insider risk incidents for consciousness campaigns and coaching. Those that are accountable for danger administration should accumulate this data. They usually seek for examples as the necessity arises. This reactive method is time consuming, nonetheless, and can lead to duplication of effort each time earlier incident knowledge is required. To minimize these points, the group ought to design its personal insider risk incident repository.
Inner improvement of an insider risk incident repository helps inform IRMP operations and, in flip, improves operational resilience extra broadly. For instance, supply-chain safety administration processes can be knowledgeable by earlier incidents captured in an insider risk incident repository. Furthermore, the repository may also help restrict popularity danger by supporting the quicker detection of incidents. Aggregated knowledge from an insider risk incident repository can spotlight potential high-risk networks or environments the place enhanced monitoring or specialised instruments must be deployed, or the place extra mitigations must be carried out.
Creating and sustaining an insider risk incident repository may be as easy or advanced as required to fulfill the group’s wants. In all instances, leveraging present requirements and practices to implement incident assortment and knowledge sharing makes the hassle related to these actions extra manageable.
Within the easiest type, an insider risk incident repository is a set of data (e.g., information, media studies) that’s organized in a repository. For instance, some organizations have a de-facto incident repository of inner incidents of their case-management system. A extra advanced repository instance is when the group makes use of the formal knowledge-management roles and obligations of its workforce to gather and retailer data in a devoted repository.
No matter its format, a number of knowledge-management actions are concerned in growing and sustaining an insider risk incident repository:
Perception that advantages the group may be derived from an insider risk incident repository in some ways. Essentially the most simple method is utilizing incidents as case research or examples for rising workforce consciousness of insider risk and coaching the workforce to acknowledge and reply to insider risk. Different methods embody root-cause evaluation, abstract statistics, pattern identification, and correlations. Every of those has its personal use instances for the insights they supply.
Every group ought to carry out some foundational analyses of its repository knowledge, particularly the components which might be associated to incidents contained in the group and inside its information-sharing partnerships. Foundational practices for deriving insights from repository knowledge may be qualitative or quantitative. An instance of a qualitative foundational apply is creating incident-repository case research to be used in coaching and consciousness actions. A quantitative instance is offering traits on how the quantity and severity of insider incidents are altering over time, which may affect risk probability and affect calculations.
Performing superior evaluation practices requires specialised information or instruments. These practices can allow robotically processing (e.g., ingesting) of incident knowledge into the insider risk incident repository. They’ll additionally present insights which might be extra advanced to derive, equivalent to advanced (or hidden) correlations between knowledge factors. For organizations utilizing technical controls, equivalent to person exercise monitoring or person and entity behavioral analytics, superior analyses must be used to refine and implement the risk fashions and risk-scoring algorithms the controls present.
Many organizations that depend on out-of-the-box configurations of those controls shortly discover that they have to tailor them to their group’s particular danger urge for food, priorities, and cultural norms. An insider risk incident repository is a crucial useful resource that a corporation can use to make sure that the IRMP’s detective functionality aligns (and continues to remain aligned) with the repeatedly altering risk panorama.
Within the COVID period, with rising numbers of staff working remotely, mitigating insider risk is extra necessary than ever. The 22 suggestions within the Information—together with the one described on this submit—are designed for resolution makers and stakeholders to work collectively to successfully stop, detect, and reply to insider threats. In a future submit, I’ll map the Information to the NIST Privateness Framework.
[ad_2]